Grid 101: Transmission 2#
Diving into how the transformer works, first, conductive wire is wrapped around an iron core. In a step-down transformer, the output wiring is wrapped around the iron core with less ‘turns’ than the input. When we go from many wiring turns to fewer, voltage decreases, such as in the illustration below. In a step up transformer on the other hand, the opposite occurs. A step-up transformer consists of a fewer primary windings with greater secondary windings.
An example of a step-down transformer:
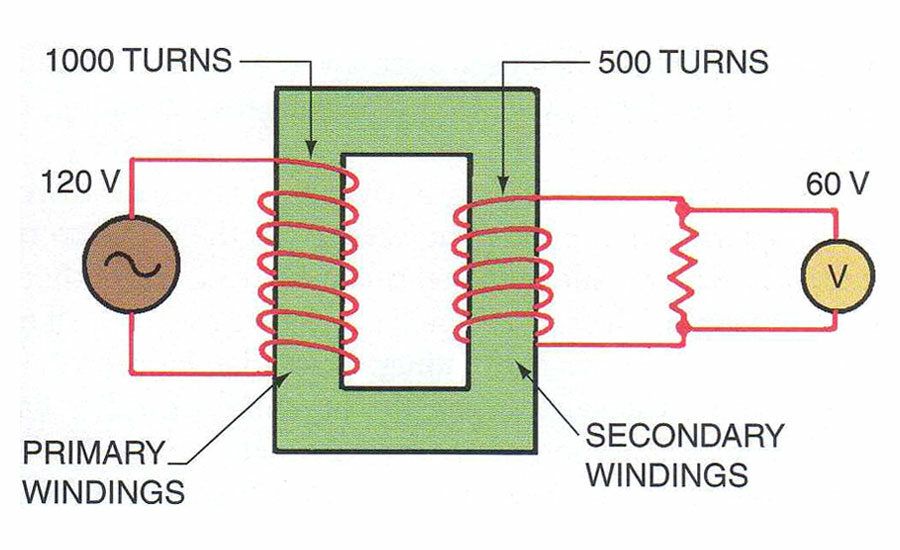
The iron core is additionally an essential part of the transformer, since they minimize unwanted currents that generate through this system, called eddy currents. While transformers found in substations are a bit differerent than the ones described above, these still demonstrate the basic principle of how a substation works.